A journal entry is a record of a financial transaction in the organization’s accounting system. It serves as the first step in the accounting cycle, documenting the details of a transaction, including the date, accounts affected, and amounts. Recording simply means putting your business’s financial transactions into your accounting records. It’s how you track the money flowing in and out of your business, usually in the form of sales and expenses but also from loans and investments. Double-entry accounting is the gold standard of financial record-keeping, used by businesses worldwide to ensure accuracy and transparency in their financial statements. While it may seem complicated at first, this system is crucial for anyone looking to keep their business finances organized and compliant with accounting standards.

How To Record Credit-Based Product Sales

Special journal is the type of journal that is created to group similar transactions together in chronological order to have better management in those transactions. The books of prime entry are the cash book, the petty cash book, the sales day book, the purchases day book and the journal. A prime entry record (or book of prime entry) is where a transaction is first recorded.
Not Reconciling Bank Statements
- If you maintain an inventory, you will have to use the accrual method, at least for sales and purchases of inventory for resale.
- Maintaining an accurate record of financial transactions through journal entries also helps businesses always be audit-ready and compliant with regulations and accounting standards.
- Strong internal controls, such as segregation of duties and dual authorization, reduce the risk of errors and fraud.
- By segregating duties and implementing approval processes, internal controls create a system of accountability that acts as a deterrent to fraudulent activities.
Recording these systems involves capturing the policies, procedures, processes, and controls that govern how financial transactions are processed and reported. This documentation not only supports internal management and operational efficiency but also plays a pivotal role in external audits, regulatory compliance, and risk management. The International Standards on Auditing (ISA) 315 emphasizes the importance of understanding and documenting internal controls as part of the risk assessment process. This article explores the methods for recording accounting and control systems, their significance, and best practices for ensuring accurate and comprehensive documentation. Accounting Records refer to organized and methodical documentation of a business’s financial transactions to create an audit trail and ensure compliance.
Recording accounting transactions without losing your mind

The primary disadvantage of the which transactions are recorded in the accounting system double-entry accounting system is that it is more complex. It also requires that mathematically, debits and credits always equal each other. This complexity can be time-consuming as well as more costly; however, in the long run, it is more beneficial to a company than single-entry accounting. On the income statement, debits increase the balances in expense and loss accounts, while credits decrease their balances. Debits decrease revenue account balances, while credits increase their balances. Reconciling accounts involves comparing entries in the general ledger with external records such as bank statements.
Sales and Purchase Recording
- This guide breaks down the accounting process into easy-to-follow steps that are repeatable every time a new accounting period begins.
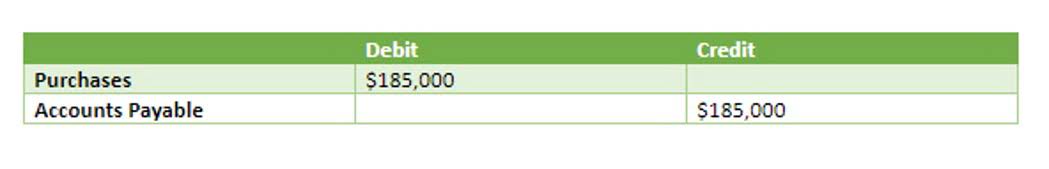
- To account for the credit purchase, a credit entry of $250,000 will be made to accounts payable.
- The books of prime entry are the cash book, the petty cash book, the sales day book, the purchases day book and the journal.
- Non-compliance with these requirements can result in legal penalties and hinder audit readiness.
- To ensure that only legal invoices are recorded and paid for, a firm has to have adequate internal controls in place.
Each of these accounts plays a significant role in tracking financial transactions and summarizing financial statements at the end of an accounting period. Small businesses often choose between cash or accrual methods of accounting. The cash method recognizes revenues and expenditures when cash is exchanged, providing straightforward tracking. In contrast, the accrual method records revenues when earned and expenses when incurred, offering a more accurate financial picture over time. Adjusting entries are necessary adjustments made to the ledger at the end of an accounting period. These entries ensure that income and expenses are accurately reported in the financial statements.
Asset Management

One frequent error is the misclassification of expenses and assets, which can distort the financial picture of a business. For example, classifying a long-term asset as an expense would inappropriately reduce profits in the short term and understate assets on the balance sheet. Examples of recorded transactions in accounting include sales invoices, purchase receipts, payroll records, bank statements, and cash receipts. These documents provide evidence of financial activities and serve as supporting documentation for financial statements. These transactions are integral to the functioning of businesses, as they manage the accounts payable and accounts receivable effectively, facilitating smooth operations. Effective management of credit transactions is crucial for maintaining a healthy cash flow and minimizing financial risks.
Credits (CR) – Debits and Credits: The Foundations of Double-Entry Bookkeeping
Journal entries must reference source documents, such as invoices or receipts, to provide evidence for each transaction. Anti-money laundering (AML) regulations also impact transaction processing. Under the Bank Secrecy Act (BSA), financial institutions must implement customer due diligence (CDD) procedures and report suspicious activities through Suspicious Activity Reports (SARs).
E. Provide Training and Promote a Documentation Culture
Accrual transactions can significantly impact the organization’s liabilities and expenses, and understanding these implications is vital for accurate financial reporting. The dual effect of transactions ensures that the accounting equation remains balanced. Each transaction affects trial balance at least two accounts, with the total debits equaling the total credits. This balance ensures that the financial records accurately reflect the assets, liabilities, and equity. Journal entries have a direct impact on an organization’s accounts, adjusting their balances based on the recorded transactions.
- Digital transactions involve electronic payment methods such as credit cards, mobile wallets, and online banking transfers.
- HighRadius is redefining treasury with AI-driven tools like LiveCube for predictive forecasting and no-code scenario building.
- These include accounts payable, accounts receivable, billings, fixed assets, payroll, and inventory.
- On this list, the total of all the debit balances must equal the total of all the credit balances.
- These small, often frequent, transactions can be overlooked or recorded incorrectly, leading to discrepancies in cash accounts.
- Understanding the different types of accounting systems is essential for any businesses and industry.
Prepare a Trial Balance
This involves documenting each transaction with details https://www.energieenwater.net/complete-the-following-comparison-table-between-4/ such as the date, accounts affected, amounts, and a brief description. Journal entries serve as the foundation of financial accounting, ensuring that all transactions are accurately captured. In the US, there is a law of the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) about businesses maintaining the accrual method. It says businesses that have sales exceeding $5 million per year and their gross receipts exceed $1 million per year must use accrual accounting method.
Account Codes – The Chart of Accounts: Organizing Accounts for Double-Entry Bookkeeping
You record an expense when you receive goods or services, even though you may not pay for them until later. Income earned in one period is accurately matched against the expenses that correspond to that period so you see a clearer picture of your net profits for each period. Using a manual accounting system means recording your transactions in a general ledger.
